Family Meals Boost Mental Health for All Ages
(NewsUSA) - Sharing a meal -- with family members that include relatives but also those you choose to call family -- not only promotes healthy eating, but healthier minds as well, new data show.
- Sharing a meal -- with family members that include relatives but also those you choose to call family -- not only promotes healthy eating, but healthier minds as well, new data show.
More than half of Americans believe that family meals make them feel more connected, according to the FMI Foundation, a nonprofit organization and creator and steward of the Family Meals Movement.
In a recent survey from the FMI Foundation, one-third of Americans said family meals make them feel calm, and approximately four in 10 said family meals are relaxing and fun, and improved their quality of life.
“These new data underscore the hundreds of studies the FMI Foundation has curated to substantiate further the expansive physical and mental health benefits of family meals,” said David Fikes, executive director of the FMI Foundation. “Sharing meals is clearly one of our best proactive practices to build a healthier nation,” he said.
Anxiety and other mental health issues have surged among youth in recent years, and FMI Foundation data support the value of family meals for giving children, teens, and young adults a way to connect and boost their feelings of well-being. Multiple published studies demonstrate that family meals are associated with reduced symptoms of depression, fewer incidents of violent behavior, and reduced thoughts of suicide in youth, as well as a reduction in patterns of disordered eating. Additional studies support the link between increased family meals and more prosocial behavior and feelings of life satisfaction among adolescents.
Family meals are good for adults, too. Data from the FMI Foundation show higher levels of self-esteem and family function, as well as lower levels of stress and depression among adults who share more meals with family members.
“Family meals are a proven way to strengthen the emotional well-being of children and adults and bolster the bonds they share.” Fikes emphasized. “With youth depression and anxiety at an all-time high, there has never been a better time to take simple steps, like family meals, to build healthier hearts, minds, and bodies.”
Joining the Family Meals Movement is one way to take advantage of the many benefits family meals offer. If you’re looking for ways to have just one more family meal each week, visit your local supermarket for meal ideas, recipes, cooking and preparation suggestions and products that help make family meals easily achievable. Many grocery stores offer in-store retail dietitians who can offer customized nutrition and meal-planning tools to fit your budget and needs. And don’t forget to take part in National Family Meals Month™, celebrated in September as part of the Family Meals Movement.
Learn more about the Family Meals Movement at www.FamilyMealsMovement.org and Family Meals Month at https://www.fmi.org/family-meals


 - Not long ago, small cell lung cancer was considered the forgotten cancer, and treatment was generally chemotherapy and radiation. But now, there is a new treatment that is showing great promise for patients with small-cell lung cancer. Some doctors say that when it works, it is like hitting a home run in treating small-cell lung cancer.
- Not long ago, small cell lung cancer was considered the forgotten cancer, and treatment was generally chemotherapy and radiation. But now, there is a new treatment that is showing great promise for patients with small-cell lung cancer. Some doctors say that when it works, it is like hitting a home run in treating small-cell lung cancer.
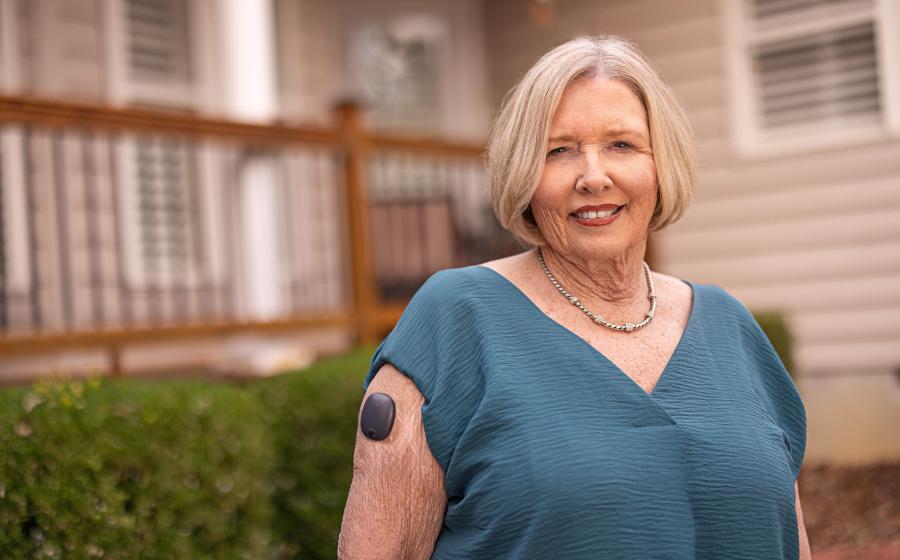

 - Dianne Mattiace shows that managing diabetes shouldn’t get in the way of enjoying your retirement, thanks in part to a game changing new technology
- Dianne Mattiace shows that managing diabetes shouldn’t get in the way of enjoying your retirement, thanks in part to a game changing new technology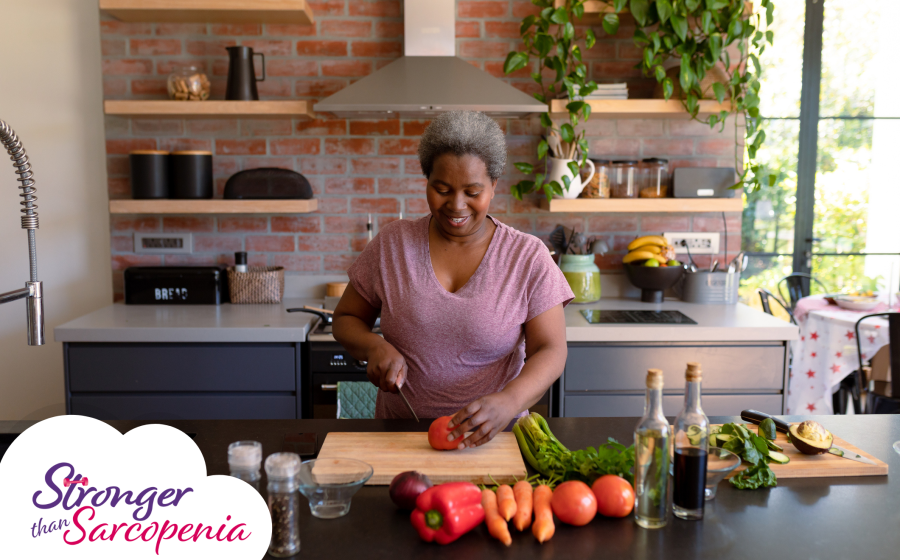
 - Age-related loss of muscle mass and strength can significantly impact the quality of life for older adults. However, recent research underscores the role of proper nutrition in preventing and managing this condition.
- Age-related loss of muscle mass and strength can significantly impact the quality of life for older adults. However, recent research underscores the role of proper nutrition in preventing and managing this condition.
 - April is National Minority Health Month, and Black Americans, American Indians/Alaska Natives (AI/AN), and underserved Americans, are among those disproportionately affected by colorectal cancer, according to the Colorectal Cancer Alliance (Alliance), the leading national nonprofit organization dedicated to ending the disease.
- April is National Minority Health Month, and Black Americans, American Indians/Alaska Natives (AI/AN), and underserved Americans, are among those disproportionately affected by colorectal cancer, according to the Colorectal Cancer Alliance (Alliance), the leading national nonprofit organization dedicated to ending the disease.
 - Obesity is an increasingly significant health problem in the United States, especially for women. The disease affects
- Obesity is an increasingly significant health problem in the United States, especially for women. The disease affects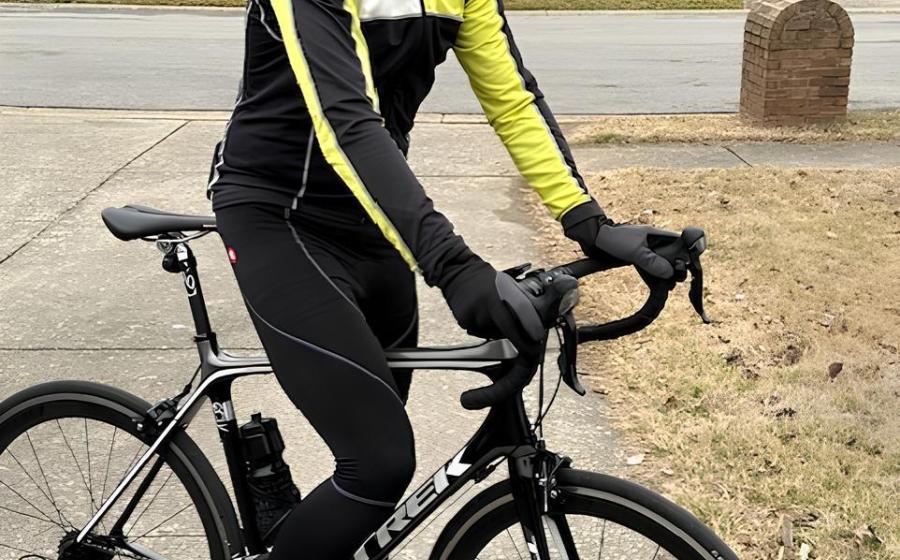 
 - It’s practically Spring, and the outdoors is calling. “I’ll be back on my bike and celebrating the return of sunny weather,” says Todd Fishman, a long-time Louisville, Kentucky, resident and devoted bicycle enthusiast. “But this year,” he notes, “I’ll be far more diligent in protecting myself from the sun’s harmful UV rays.”
- It’s practically Spring, and the outdoors is calling. “I’ll be back on my bike and celebrating the return of sunny weather,” says Todd Fishman, a long-time Louisville, Kentucky, resident and devoted bicycle enthusiast. “But this year,” he notes, “I’ll be far more diligent in protecting myself from the sun’s harmful UV rays.” 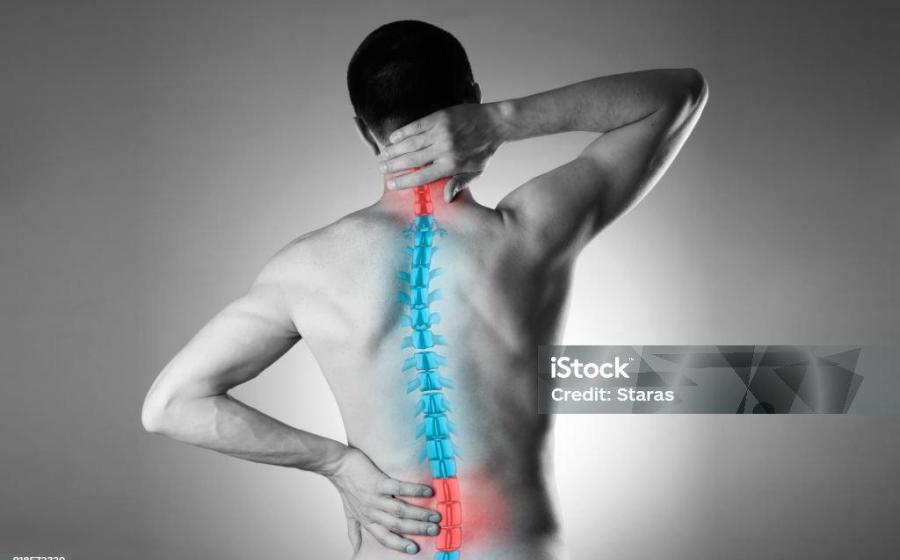
 - Low back pain remains a leading cause of disability and missed time from work in the United States. However, an at-home traction device offers a path to relief, according to Dr. Jeff Fisher, an Irvine, California-based chiropractor with more than 30 years of experience. Dr. Fisher invented the Fisher Traction Neck Device after experiencing an acute spine-related sports injury. Several years later, he developed the Fisher Traction Low Back Device to help his wife and sons manage herniated discs at home.
- Low back pain remains a leading cause of disability and missed time from work in the United States. However, an at-home traction device offers a path to relief, according to Dr. Jeff Fisher, an Irvine, California-based chiropractor with more than 30 years of experience. Dr. Fisher invented the Fisher Traction Neck Device after experiencing an acute spine-related sports injury. Several years later, he developed the Fisher Traction Low Back Device to help his wife and sons manage herniated discs at home.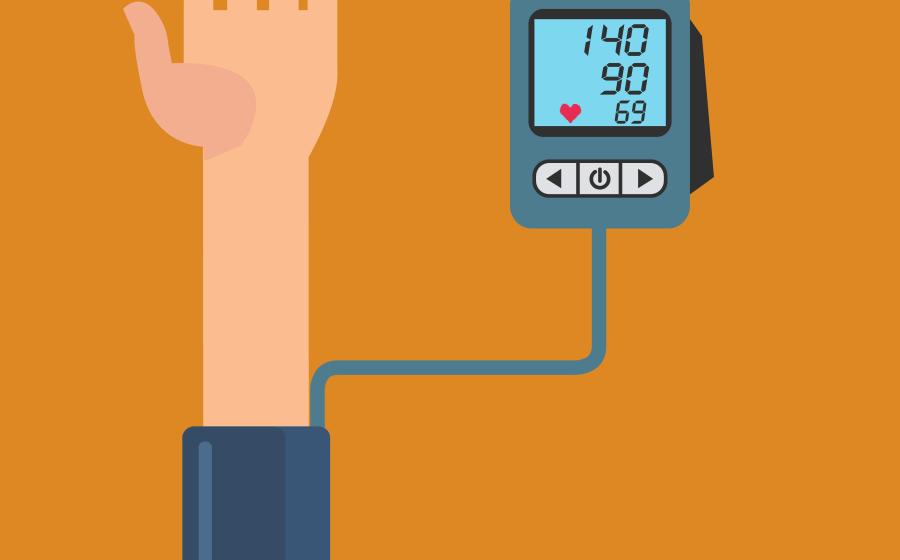
 - La presión arterial alta, también conocida como hipertensión, es una epidemia creciente que afecta a la mitad de todos los estadounidenses. La presión arterial alta puede dañar órganos vitales como el corazón, el cerebro, los riñones y los ojos sin ninguna señal de advertencia. Si no se trata, también puede provocar problemas graves como dolor de pecho, ataques cardíacos e insuficiencia cardíaca, y aumenta el riesgo de accidente cerebrovascular y enfermedad renal crónica. Durante mucho tiempo, la única forma de tratar la presión arterial alta era mediante cambios en el estilo de vida, como dieta y ejercicio, o tomando medicamentos. Hoy en día, hay otro enfoque a considerar además de las modificaciones en el estilo de vida y los medicamentos.
- La presión arterial alta, también conocida como hipertensión, es una epidemia creciente que afecta a la mitad de todos los estadounidenses. La presión arterial alta puede dañar órganos vitales como el corazón, el cerebro, los riñones y los ojos sin ninguna señal de advertencia. Si no se trata, también puede provocar problemas graves como dolor de pecho, ataques cardíacos e insuficiencia cardíaca, y aumenta el riesgo de accidente cerebrovascular y enfermedad renal crónica. Durante mucho tiempo, la única forma de tratar la presión arterial alta era mediante cambios en el estilo de vida, como dieta y ejercicio, o tomando medicamentos. Hoy en día, hay otro enfoque a considerar además de las modificaciones en el estilo de vida y los medicamentos. 
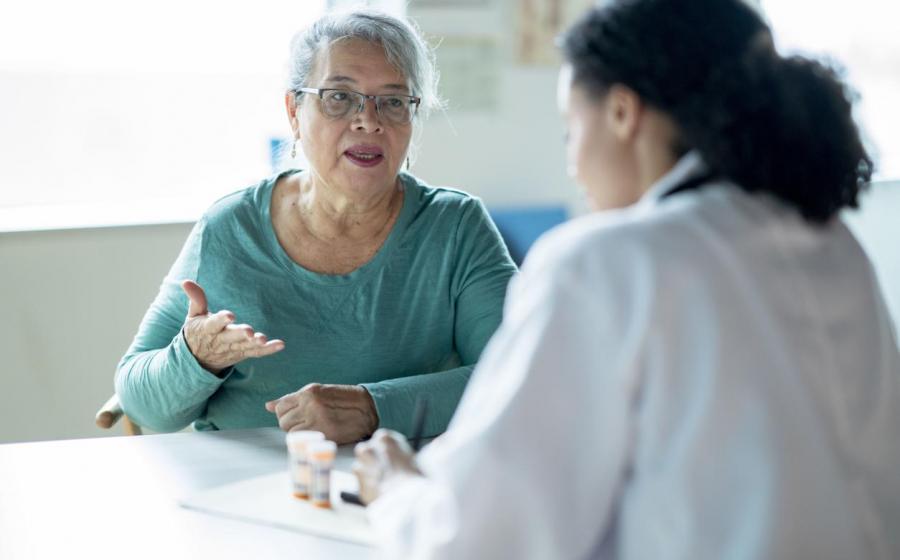

 - In the ongoing battle against COVID-19, vaccines have been successful in helping to reduce illness and contributing to the declining numbers of infections in the U.S. and around the world. But COVID-19 is not gone, and it remains a significant threat. Those with weakened immune systems, chronic illnesses and other risk factors are particularly vulnerable to severe illness from the virus.
- In the ongoing battle against COVID-19, vaccines have been successful in helping to reduce illness and contributing to the declining numbers of infections in the U.S. and around the world. But COVID-19 is not gone, and it remains a significant threat. Those with weakened immune systems, chronic illnesses and other risk factors are particularly vulnerable to severe illness from the virus.